Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy (IgAN)
Jump to topic
IgAN is an autoimmune glomerulonephritis with heterogeneous clinical presentation, variable disease progression, and multiple underlying mechanisms.1-6 Learn more about its burden of disease and pathogenesis below.
At a glance: Multi-hit model of IgAN
ExploreTest your knowledge
Your score:
0True or false? IgAN is the most common form of primary glomerulonephritis worldwide.
To learn more, choose the answer that you find the most likely:
Show me the answer
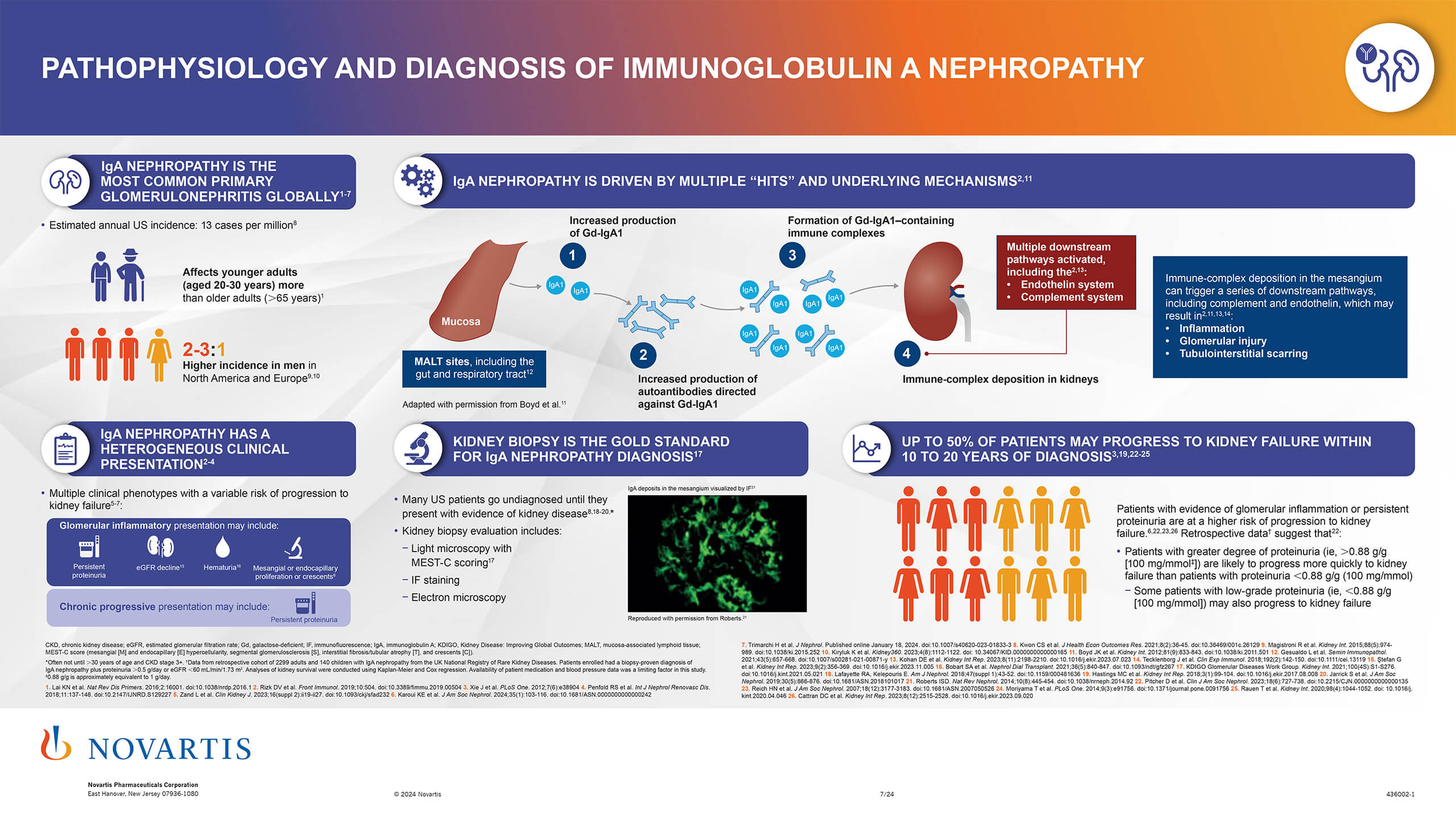
IgAN is the most common form of primary glomerulonephritis worldwide and the leading cause of kidney failure in young White adults in the United States.1,2 IgAN incidence is higher in children and young adults (aged 20-30 years) than in older adults (aged >65 years) and is unequally distributed between sexes worldwide.1,3 In Europe and the United States, IgAN affects males more often than females (3:1), whereas IgAN is more evenly distributed between sexes in east Asia (1:1).3
Which of the following statements is false regarding IgAN?
To learn more, choose the answer that you find the most likely:
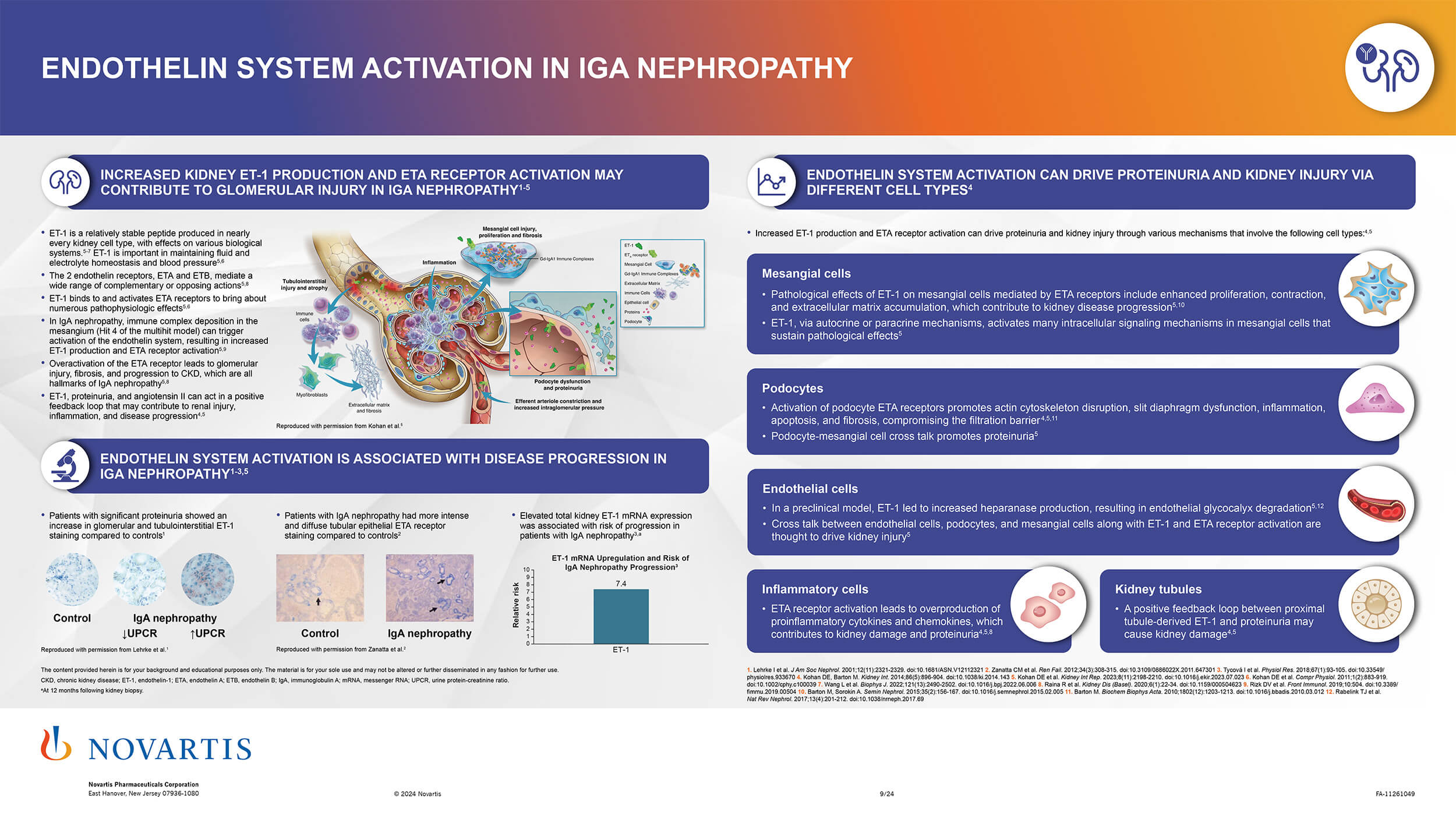
- a Complement system activation is implicated in the “multi-hit model” of IgAN pathogenesis
- b IgAN diagnosis is based on detection of IgA deposits by kidney biopsy
- c IgAN and IgA vasculitis (IgAV) have indistinguishable clinical presentation
Show me the answer
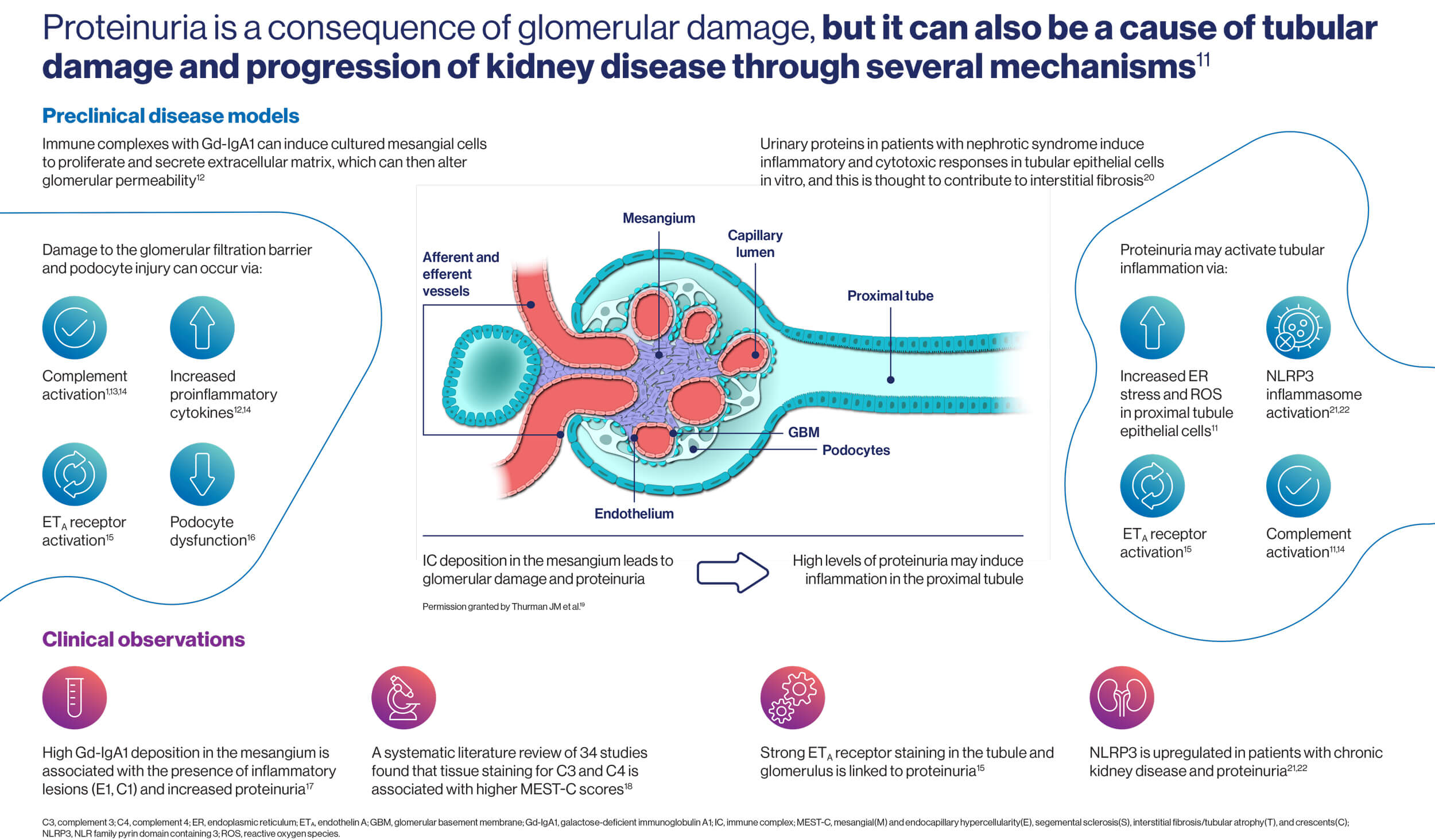
Immune complex formation and activation of the alternative, and sometimes lectin, complement pathway contribute to glomerular injury in IgAN.1,2 Diagnosis is dependent on kidney biopsy to identify IgA deposition in the glomerular mesangium and no specific, validated diagnostic laboratory tests are available.3-5 Although IgAN and IgAV (previously known as Henoch-Schönlein purpura) present with similar kidney pathology, IgAV has distinct clinical signs affecting the skin, joints, and intestines.3,5
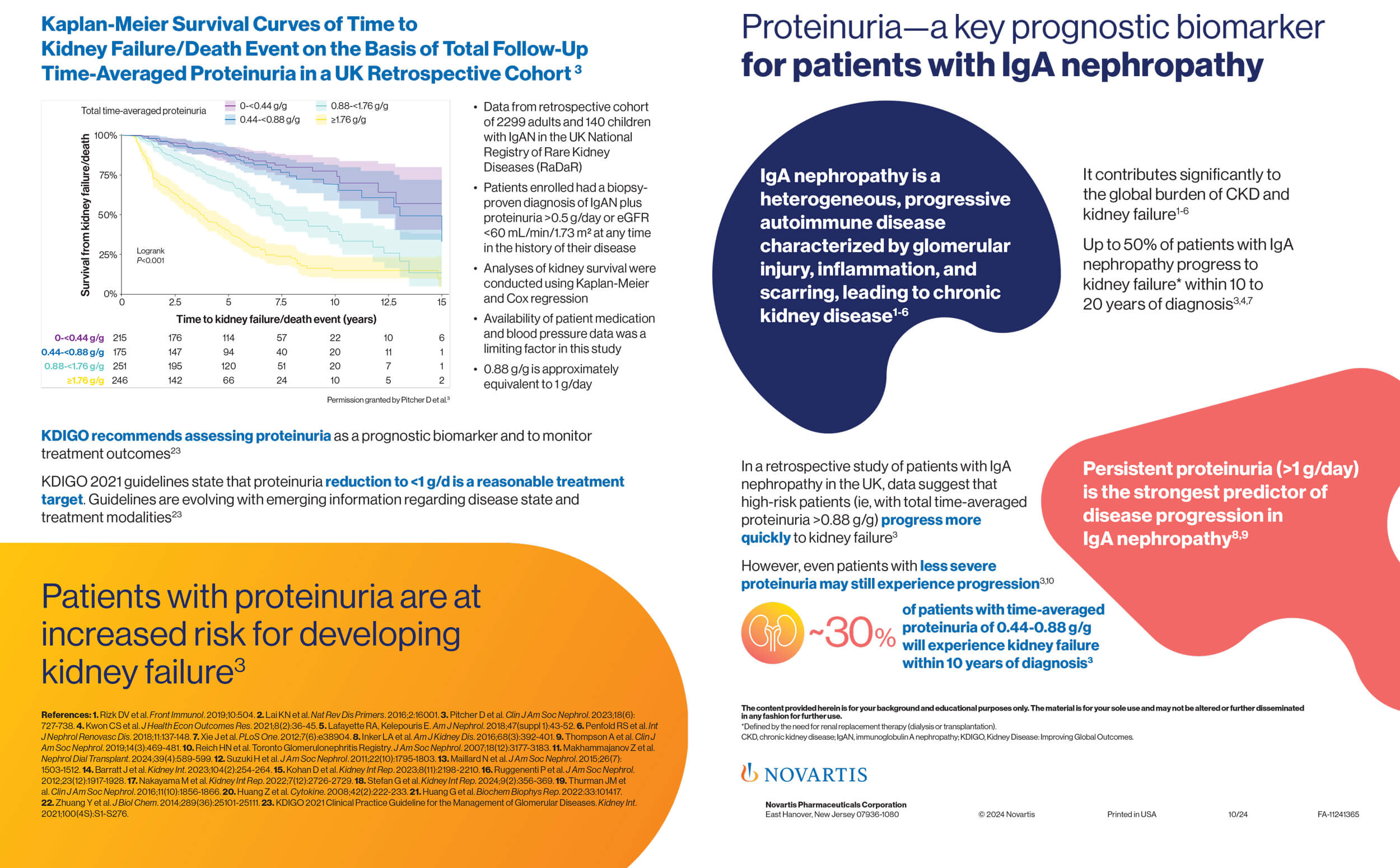
For IgAN patients with 2 to 3 g/day proteinuria, what incidence of progression to ESKD has been observed after 5 years of follow-up?
To learn more, choose the answer that you find the most likely:
Show me the answer
Disease progression to ESKD in patients with 2 to 3 g/day proteinuria is 20%. Proteinuria can be an important prognostic indicator in patients with IgAN. The Toronto IgAN registry followed 542 patients for 78 months; the graph demonstrates proteinuria >1 g/day is an established risk factor for poor prognosis in patients with IgAN. Renal survival with >3 g/day proteinuria is significantly worse.
References
- Lai KN et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16001.
- Rizk DV et al. Front Immunol. 2019;10:504.
- Zand L et al. Clin Kidney J. 2023;16(2):ii19-ii27.
- Karoui KE et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024;35(1):103-116.
- Boyd JK et al. Kidney Int. 2012;81(9):833-843.
- Kohan DE et al. Kidney Int Rep. 2023;8(11):2198-2210.